- 50 types of fully vector 1D, 2D and Post barcodes
- QR code design editor and ready-made styles
- loading data from a barcode for editing
- VCard, meCard, WiFi and other QR code types for smartphones
The plugin is designed to create various types of barcodes in CorelDraw. Unlike standard tools,
all codes are formed in a vector form, preserving data encoded in them,
thus providing the possibility of editing in the future
.
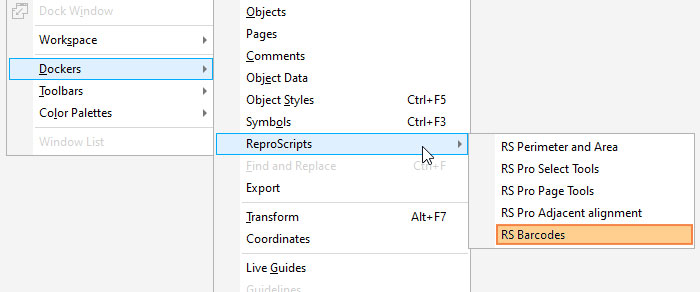
After installing the plugin, a new Barcodes item appears in the Windows > Dockers > ReproScripts menu allowing you to open the docker.
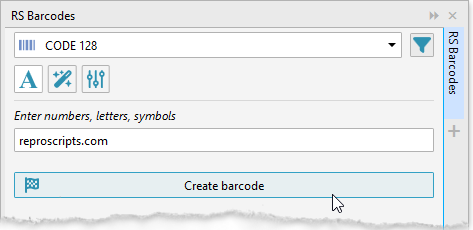
Barcode type selection and configuration
At the top of the panel there is a drop-down list of supported barcode types. Depending on what kind of code you want to generate, you can set the appropriate value and additional parameters.
Barcode setup
Data and barcode rendering parameters are managed in three tabs, which are switched using buttons with icons.
 Barcode value tab
Barcode value tab
When this tab is active, you can set the value that needs to be encoded in the barcode.
In most cases, this is one text field, above which there is brief information about which characters and their number can be encoded in this type of barcode.
The plugin performs basic data validation and blocks the start of code generation for obviously incorrect values.
Additional data entry options are available for the QR code, which are described below.
 Barcodes design tab
Barcodes design tab
The design tab is available for all barcode types and, at a minimum, allows you to control the color of the lines and background of the generated code, as well as its orientation. For a QR code, you can control its design, which is described below.
 Barcodes parameters tab
Barcodes parameters tab
Most barcodes have additional parameters that affect the code generation process. They can be managed in the last tab.
Many 1D barcodes also allow a text representation of the data to be placed below the code. If available, you can adjust the text size, font, and alignment in the params tab.
Setting up a QR code
The QR code parameters are significantly different from other types and contain more options.
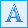
 QR code value
QR code value
In the value panel for a QR code, you can select the type of data that will be encoded in it.
In addition to just text, you can encode other types of data. The plugin collects and performs basic data validation for each value type and encodes it into a QR code.
| QR Value type |
Description |
|
Text
|
Any text value that can contain up to 4296 alphanumeric characters, 7089 numeric characters.
|
|
Web address
|
The address of a website or other Internet resource. The plugin checks the basic structure of the address and does not accept obviously incorrect values.
|
|
vCard
|
This is a file format standard for electronic business cards. In this format, you can encode both business and personal data, which can then be read on a smartphone and entered into the address book.
|
|
meCard
|
Another format for exchanging contact information for smartphones. Contains only the minimum required fields, allowing you to create more compact and better readable codes.
|
|
WiFi
|
The QR code will contain the data necessary to connect to the WiFi network without the need to enter data manually. Supported by all modern smartphones.
|
|
Location
|
Encoded geolocation, suitable for reading and further building a route in navigation applications.
|
|
Calendar event
|
Data for generating an event suitable for use with various calendar applications. A universal code is generated that is recognized by Google, Apple and other calendars.
|
|
Email
|
Generates code to quickly prepare a message for sending by email.
|
|
SMS
|
Generates a code for quickly preparing a message as an SMS.
|
|
Crypto Transfer
|
A QR code indicating the crypto wallet details for receiving transfers. May or may not contain the amount being transferred.
|
 QR code design
QR code design
 WATCH VIDEO: Designer QR codes in CorelDraw
WATCH VIDEO: Designer QR codes in CorelDraw
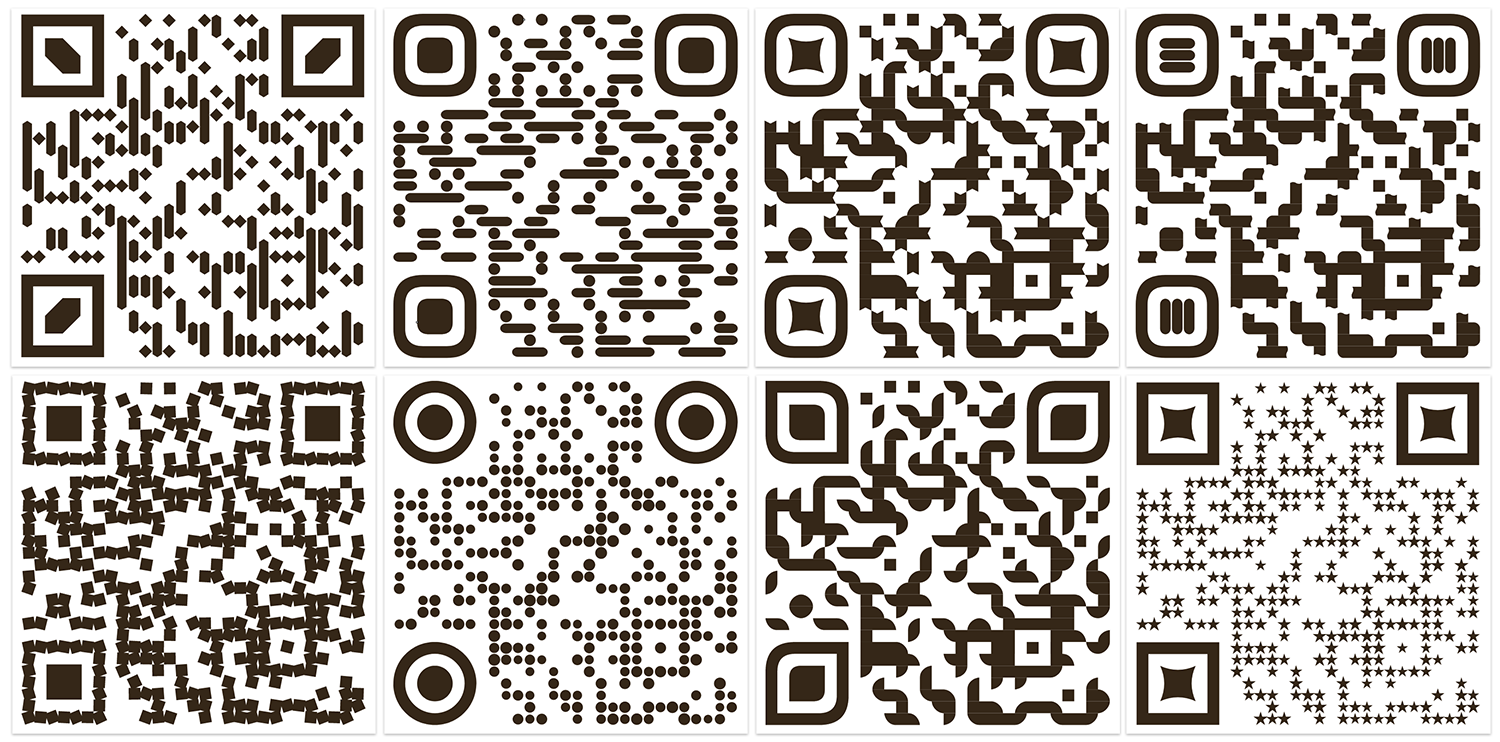
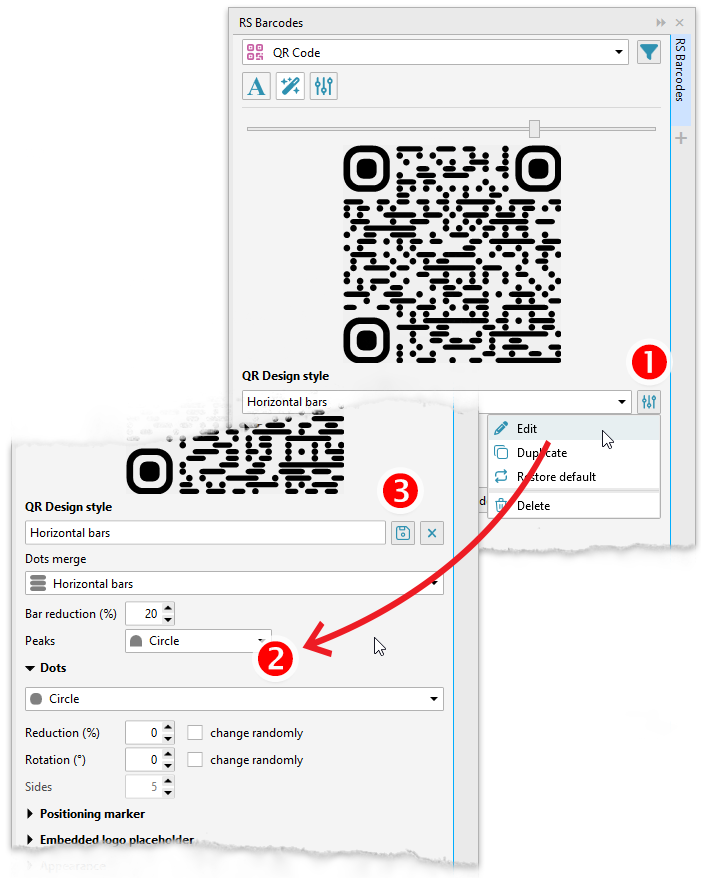
Design styles
In the barcode design panel, you can specify the QR code style. It includes various parameters that allow you to radically change the appearance of the finished code. The panel contains a preview window in which you can immediately see how the code will look when designed in one style or another.
The plugin comes with several standard styles that you can use right away. Based on these styles, you can create your own. To do this, in the side menu of the style list, you can duplicate it or open it for editing. 1 In the editor that opens, you can select and configure various parameters 2 that affect the appearance of the QR code — the method of grouping points, their shape and variations, the shape and design of peaks, corner and register elements. This opens up rich possibilities for managing the design of the QR code and compiling your own library of QR code styles. Both standard and custom styles can also be used when generating variable data in the ReproScripts VDP plugin. You can save the finished style by giving it a suitable name or immediately generate the code from the style editor. 3
Placeholder for a logo
The plugin also allows you to calculate and create a place in the center that can be used to place a logo. By activating this option, you can set the shape and aspect ratio that is required for your logo. The plugin will set the maximum level of error correction for the QR code and calculate the area that can be safely allocated for the logo without affecting the readability of the QR code. You can place your logo or other suitable image in the space allocated by the plugin.
How to create and edit a barcode
 WATCH VIDEO: Vector editable barcodes in CorelDraw
WATCH VIDEO: Vector editable barcodes in CorelDraw
After setting the desired values, the Create barcode button is activated, clicking on which you can form a barcode.
The plugin will create a new document if there is no active one at the moment. The new barcode is by default placed into the center of the page. But
if there is a CorelDraw shape selected, the plugin will take its size, position and rotation angle and apply these values to the newly created code. This allows to easily manage the size and position of codes in the design.
Editing barcodes
Each barcode, prepared by the plugin can be edited later. If it is selected in the document, additional buttons Pick value and Update appear in the docker.
The Pick up button allows to read and load from the barcode in the docker. After making changes, you can click the Update button and a new the barcode will be replaced with new one. This way you can easily edit barcodes without having to re-enter the data encoded in them every time.
List of barcodes supported by the plugin
AZTEC
A 2D matrix code with high data capacity and error correction. Popular in mobile applications and QR-like scenarios. Supports HIBC variant.
Can encode up to a maximum length of approximately 3823 numeric or 3067 alphabetic characters.
Popularity: 7/10
Applications: Transportation (e-tickets, boarding passes), healthcare (patient records), and digital payments.
Supported variants:
Compact

AZTEC RUNES
A compact version of Aztec Code for small data (numeric only) for encoding whole integers between 0 and 255.
Popularity: 1/10
Applications: Experimental or niche applications, limited real-world use.
DataMatrix
A 2D matrix code with high data density. Supports HIBC variant. The barcode can encode a large amount of data in a small area.
The largest version of DataMatrix 24 (144 x 144) can encode 3116 digits, around 2335 alphanumeric characters, or 1555 bytes
of data.
Popularity: 8/10
Applications: Electronics, aerospace, healthcare, and logistics.
DotCode
A 2D matrix code designed for rapid scanning. Used in AIM standards for specific industries.
DotCode uses a grid of dots in a rectangular formation to encode characters up to a maximum of approximately
450 characters (or 900 numeric digits).
Popularity: 4/10
Applications: Tobacco industry, high-speed printing, and logistics.
Grid Matrix
A 2D matrix code developed for Chinese markets, less common globally.
Grid Matrix groups modules in a chequerboard pattern, and by default supports Hanzi, ASCII and a small number of ISO 8859-1 characters.
Up to around 1529 alphanumeric
characters or 2751 digits may be encoded.
Popularity: 3/10
Applications: Chinese logistics and electronics.
GS1 DataMatrix
GS1 DataMatrix is a 2D barcode standard that follows GS1 specifications, encoding structured data like product IDs, serial numbers, and expiration dates for supply chain use. It includes a Function 1 (FNC1) character to indicate GS1 formatting, ensuring compatibility with GS1 standards for global trade.
Popularity: 8/10
Applications: Common for GS1 applications.
Han Xin Code
A 2D matrix code optimized for Chinese characters, limited global use.
The largest version 84 (189x189) can encode 7827 digits, 4350 ASCII characters, up to 2175 Chinese characters.
Popularity: 4/10
Applications: Chinese logistics, healthcare, and government.
MaxiCode
A 2D matrix code with hexagonal modules, specific to high-speed sorting.
MaxiCode symbols can be encoded in one of five modes.
The maximum length of text that can be placed in a MaxiCode symbol depends on the type of characters used
in the text and ranges from 84 to 138.
Popularity: 5/10
Applications: UPS and logistics for package tracking.
PDF147
PDF417 is a 2D stacked barcode that can encode large amounts of data, up to 1,850 alphanumeric characters or 2,710 numeric digits. It consists of multiple rows of linear bar patterns, with a configurable number of rows (3 to 90) and columns (1 to 30). PDF417 supports adjustable error correction (up to 9 levels) for reliable scanning, even if damaged. It’s widely used in applications like ID cards, tickets, and logistics due to its high data capacity and versatility.
Popularity: 7/10
Applications: Driver’s licenses, logistics, and ticketing.
Supported variants:
Compact
 Micro
Micro

QR code
QR Code is a 2D matrix barcode capable of encoding up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters. It features a square grid with three alignment patterns for fast scanning. QR Codes support four error correction levels (L, M, Q, H), allowing data recovery even if partially damaged. Widely used for URLs, contact info, and payments, its versatility and readability make it ideal for consumer and industrial applications.
Popularity: 10/10
Applications: Marketing, payments, ticketing, and digital interfaces.
Micro QR code
Micro QR Code is a compact 2D barcode designed for small spaces, encoding up to 35 numeric or 21 alphanumeric characters. It’s a smaller version of the QR Code, with sizes ranging from 11x11 to 17x17 modules and is ideal for applications like product labeling or electronics where space is limited. Unlike standard QR Codes, it has only one position detection pattern, simplifying scanning on small surfaces.
Popularity: 5/10
Applications: Electronics and small product labeling.
Rectangular Micro QR code
Rectangular Micro QR Code is a variant of the Micro QR Code, designed for small, rectangular spaces. It encodes up to 35 numeric or 21 alphanumeric characters, with sizes ranging from 11x9 to 17x13 modules. Like the standard Micro QR, it uses one position detection pattern for efficient scanning and supports four error correction levels (L, M, Q, H). It’s ideal for compact labeling on products or components where a rectangular shape fits better than a square.
Popularity: 4/10
Applications: Narrow packaging and electronics.
CODE 11
Popularity: 2/10
Applications: Telecommunications equipment labeling.
Code 11 is a linear barcode symbology developed for high-density numeric data, primarily used in telecommunications. It encodes digits 0-9 and a dash (-), with each character represented by a unique pattern of bars and spaces. Code 11 uses a variable length format and includes one or two check digits for error detection, making it suitable for applications requiring reliable numeric encoding.
CODE 128
Popularity: 9/10
Applications: Shipping, logistics, retail, and inventory management.
Code 128 is a high-density, linear barcode symbology used for alphanumeric data. It can encode all 128 ASCII characters, including numbers, letters, and symbols, using a compact format. Code 128 supports three subsets (A, B, C) for flexible encoding and includes a check digit for error detection. Widely used in logistics, shipping, and inventory management, it offers versatility and reliability.
CODE 39
Popularity: 7/10
Applications: Automotive, defense, and general-purpose labeling.
Code 39 is a linear barcode symbology designed for alphanumeric data, encoding digits 0-9, uppercase letters A-Z, and a few special characters (e.g., -, ., *, $). Each character is represented by a pattern of wide and narrow bars and spaces. Code 39 is variable-length, self-checking, and widely used in industries like manufacturing and logistics for its simplicity and readability.
CODE 93
Popularity: 3/10
Applications: Canadian postal services and some logistics.
Code 93 is a compact, linear barcode symbology designed for alphanumeric data, encoding digits 0-9, uppercase letters A-Z, and select special characters. An enhanced version of Code 39, it offers higher density and improved reliability with two check digits for error detection. Code 93 is variable-length and widely used in logistics, inventory, and postal applications for its efficiency and readability.
EAN-13
- EAN-13: 13 digits, the primary standard for most products, with a full product code.
- EAN-8: 8 digits, used for smaller items, with a condensed product code.
- EAN-5: 5 digits, a supplemental code for additional data (e.g., price, issue number).
- EAN-2: 2 digits, a shorter supplemental code for limited extra information (e.g., magazine issues).
EAN-14
Popularity: 6/10
Applications: Logistics and wholesale for carton identification.
EAN-14, also known as GTIN-14, is a 14-digit barcode standard used primarily for identifying trade items at the case or pallet level in supply chains. It extends the EAN-13 format by adding a leading digit (indicator) to represent packaging levels or other attributes. Encoded in an ITF-14 or GS1-128 barcode, it facilitates inventory management, logistics, and traceability in global commerce.
GS1 128
Popularity: 8/10
Applications: Widely adopted in global supply chains due to its versatility, particularly in shipping and warehouse management.
GS1-128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology, a subset of Code 128, used globally in supply chains for encoding detailed product information like batch numbers, expiration dates, and serial shipping container codes (SSCC). It employs Application Identifiers (AIs) and a Function Code 1 (FNC1) character to define data types, ensuring interoperability and traceability in industries such as logistics, retail, and healthcare.
GS1 DataBar Truncated

GS1 DataBar is a family of linear barcode symbologies designed for compact data encoding, primarily used in retail, grocery, and healthcare for small items or variable measure products. It supports GS1 Application Identifiers (AIs) to encode data like product IDs, weights, or expiration dates.
Popularity: 6/10
Applications: Moderately popular in retail and grocery for small or variable items.
Supported variants:
Limited

Extended

- GS1 DataBar Truncated: A shorter-height version of GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional, used where space is limited but scanning requires omnidirectional capability. It encodes up to 14 digits, typically for product identification.
- GS1 DataBar Limited: A compact barcode with restricted data capacity (up to 14 digits) and specific constraints on leading digits (0 or 1), used for small retail items with limited space, like loose produce.
- GS1 DataBar Expanded: A more versatile version that can encode up to 74 numeric or 41 alphanumeric characters, including additional data like lot numbers or dates, suitable for complex retail or healthcare applications.
Interleaved 2 of 5
Popularity: 5/10
Applications: Used in specific applications like logistics and film processing.
Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) is a continuous, two-width barcode symbology that encodes digits in pairs, using five bars (two wide) for the first digit and five spaces (two wide) for the second. It is compact, ideal for numeric data, and used in logistics, retail (e.g., ITF-14 for cartons), and 135 film canisters. It supports variable lengths and optional check digits for accuracy.
ISBN
Popularity: 9/10
Applications: Extremely popular and universally adopted in the global publishing and bookselling industries.
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a unique numeric identifier for books, encoded in a barcode (typically EAN-13 or UPC-A) for retail and library use. It consists of 10 or 13 digits, representing the country, publisher, title, and a check digit. ISBN facilitates inventory management, sales tracking, and cataloging in the publishing industry.
ITF-14
Popularity: 7/10
Applications: Widely used in retail and logistics for outer packaging.
ITF-14 (Interleaved 2 of 5, variant 14) is a numeric barcode symbology used primarily for encoding Global Trade Item Numbers (GTIN-14) on shipping cartons and pallets in retail and logistics. It encodes 14 digits, including a packaging indicator, product identifier, and check digit, designed for high-volume scanning in supply chains. Its robust design ensures readability even when printed on corrugated surfaces.
PharmaCode One-Track

PharmaCode, also known as Pharmaceutical Binary Code, is a 1D barcode standard used in the pharmaceutical industry for packaging control. Developed by Laetus, it encodes numeric data in binary format using bars of varying widths, designed to be readable despite printing errors. It is not used for point-of-sale but for in-house inventory and security verification.
Popularity: 4/10
Applications: Primarily used in pharmaceutical packaging for internal control, with limited adoption outside this sector.
Supported variants:
Two-Track

- PharmaCode One-Track: The standard PharmaCode, it uses a single row of bars (thick and thin) to encode integers from 3 to 131070, read typically from right to left. It supports color bars for print verification and has a miniature version for limited space. It is used for matching packaging materials and contents.
- PharmaCode Two-Track: A variant that uses two rows of bars, combining full and half-height bars vertically to encode integers from 4 to 64570080. It also reads right to left and is designed for enhanced data capacity in pharmaceutical packaging control.
Plessey Code

A 1D linear barcode developed in 1971 by The Plessey Company (UK), using pulse-width modulation. It encodes hexadecimal digits with a simple pattern of wide/narrow bars and spaces, featuring a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) for error detection. Primarily used for inventory, such as supermarket shelf tags. Popularity: 3/10 (rarely used today, mostly in niche applications like libraries or retail stock control).
Popularity: 3/10
Applications: Retains moderate use in inventory systems.
Supported variants:
Plessey UK

- MSI Plessey (Modified Plessey):Developed by MSI Data Corporation, based on Plessey Code. A numeric-only, variable-length barcode using binary encoding (black bars = "1", spaces = "0") with an optional check digit (commonly Mod-10). It’s continuous, not self-checking, and used for inventory tracking in warehouses and retail.
- UK Plessey: It’s essentially the same as Plessey, with no significant structural differences, used historically in the UK for retail restocking (e.g., by J.Sainsbury).
UPC-A

A 1D linear barcode (Universal Product Code, version A) encoding 12 numeric digits, including a manufacturer code, product code, and a Mod-10 check digit. Widely used in retail for product identification at point-of-sale (e.g., supermarket scanners). Structured with guard bars, left and right digit sets, and a center pattern for reliable scanning.
Popularity: 9/10
Applications: Ubiquitous in global retail, especially in North America, due to its standardization and compatibility.
Supported variants:
UPC-E

- UPC-E: A compressed version of UPC-A, encoding 6-8 numeric digits (depending on compression) for smaller packages. It omits some digits from UPC-A (via zero-suppression rules) while maintaining compatibility with UPC-A scanners. Includes a check digit and is used for space-constrained retail items.
VIN
Popularity: 8/10
Applications: Widely used in the automotive industry globally for vehicle tracking and documentation, but limited to this sector.
The VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) barcode is a 1D linear barcode, typically using Code 39 or Code 128, to encode a 17-character alphanumeric VIN. The VIN uniquely identifies vehicles, including manufacturer, model, year, and serial number, following ISO 3779 standards. Barcodes are used for efficient scanning in automotive manufacturing, inventory, and registration processes.
Australia Post 4-State
Customer

Redirect

Reply
Routing
The Australia Post 4-State barcode is a variable-length, alphanumeric 1D barcode used by Australia Post for postal code and automatic mail sorting. It features four bar types (Full, Tracker, Ascender, Descender) and Reed-Solomon error correction, encoding 37 to 67 bars depending on the format. It supports numeric (0-9), alphabetic (A-Z, a-z), space, and hash (#) characters, with a quiet zone of 6 mm on sides and 2 mm above/below. The barcode enhances mail processing efficiency through high data density and readability.
Deutsche Post
Leitcode

Identcode

The Deutsche Post barcode is used for mail and parcel tracking in Germany, primarily through two formats: Leitcode and Identcode.
Both use the Code 128 symbology, ensuring compatibility with Deutsche Post’s automated sorting systems.
- Leitcode: A 14-digit barcode used for sorting and routing mail within Germany. It encodes the postal code (5 digits), street/house number (3 digits), and a product code (6 digits). It ensures accurate delivery by providing location-specific data.
- Identcode: A 12-digit barcode used for tracking individual mail items, such as registered letters or parcels. It includes a mail item number, customer ID, and check digit, enabling precise tracking and verification during transit.
Dutch Post KIX Code
The Dutch Post KIX Code (Klantenindex) is a four-state barcode used by PostNL, the Netherlands postal service, for automated mail sorting. It encodes alphanumeric characters (0-9, A-Z) representing a Dutch postal code (6 characters), house number (up to 5 digits), and an optional suffix (up to 6 characters) separated by an "X". Based on the Royal Mail 4-State Customer Code (RM4SCC), it omits start/stop bars and checksums, using four bar types (ascender, descender, tracker, or both) to form a 36-character alphabet. Printed below the address, it enables efficient machine-readable sorting and offers postage discounts for bulk mail.
Japanese Postal Barcode
The Japanese Postal Barcode, also known as the Japan Post 4-State Customer Code, is a four-state barcode used by Japan Post for automated mail sorting. It encodes a 7-digit postal code (e.g., 108-0075, hyphen not encoded) and an optional address indication of up to 13 alphanumeric characters (0-9, A-Z, hyphen). The barcode consists of four bar types (ascender, descender, full, or tracker), with start bars (FD), stop bars (DF), and a check digit. It requires a 2 mm quiet zone and is positioned parallel to the mail edge, typically below or beside the address, for efficient processing.
Korea Post Barcode
The Korea Post Barcode, also known as the Korean Postal Authority Code, is a barcode used by Korea Post for automated mail sorting. It encodes a 5-digit postal code, utilizing the horizontal positioning of bars to represent numeric digits (0-9). Based on the 4-state barcode system, it facilitates efficient processing of mail within South Korea.
Royal Mail
Customer
Mailmark

2D Mailmark

The Royal Mail Barcode is used by the UK’s Royal Mail for automated mail sorting and tracking, primarily based on the Royal Mail 4-State Customer Code (RM4SCC). It encodes alphanumeric data (0-9, A-Z) using four bar types (ascender, descender, tracker, full) to represent postal codes and delivery details.
All variants are machine-readable, designed for high-speed sorting, and include error-checking mechanisms. They require a quiet zone around the barcode and specific placement on mail items.
- Customer Barcode (RM4SCC):The standard 4-state barcode encodes a UK postcode (e.g., SW1A 1AA) and a delivery point suffix (DPS, e.g., 1A). It includes start/stop bars and a checksum for error detection, enabling efficient sorting of letters and parcels. Typically printed below the address, it supports bulk mail discounts.
- Mailmark Barcode: An advanced version of RM4SCC, Mailmark uses the same 4-state structure but includes additional data for enhanced tracking and reporting. It encodes a unique item ID, supply chain ID, and destination details. Available in 2D and 4-state formats, it provides real-time mail tracking and delivery insights for businesses, requiring pre-registration with Royal Mail.
- Mailmark 2D Barcode: A Data Matrix (2D) barcode variant of Mailmark, it stores more data in a compact square format. It encodes similar information as the 4-state Mailmark (item ID, destination, etc.) but is ideal for smaller mail items or labels with limited space. It supports high-density data and advanced tracking features.
USPS Intelligent Mail
The USPS Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMb) is a 4-state barcode used by the United States Postal Service (USPS) for sorting, tracking, and managing mail and packages. It encodes up to 31 digits, including a 20-digit tracking code (Barcode ID, Service Type ID, Mailer ID, Serial Number) and an 11-digit delivery point ZIP code (ZIP+4 plus delivery point). Using four bar types (ascender, descender, tracker, full), it replaces older POSTNET and PLANET barcodes, offering enhanced data capacity and precision. The IMb supports automated sorting, real-time tracking, and delivery confirmation, with a required quiet zone and specific placement on mailpieces.
 Barcode value tab
Barcode value tab
 Barcodes design tab
Barcodes design tab Barcodes parameters tab
Barcodes parameters tab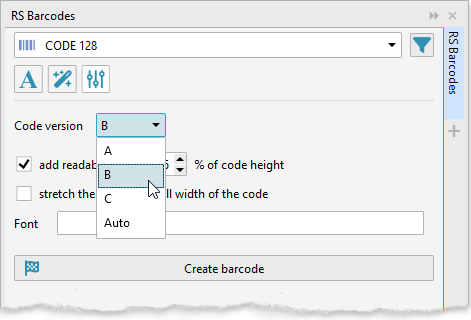
 QR code value
QR code value
 QR code design
QR code design WATCH VIDEO: Designer QR codes in CorelDraw
WATCH VIDEO: Designer QR codes in CorelDraw


 WATCH VIDEO: Vector editable barcodes in CorelDraw
WATCH VIDEO: Vector editable barcodes in CorelDraw